Content
Help 1: Energy units
You are probably familiar with using Joule as a measure of energy. In particle physics, however, we use something called electron volt (eV)
instead . The reason we use this is that the energies we are measuring in particle collisions are very small and are related to the
energies of single particles. The definition of an electron volt is the kinetic energy a single electron gets by moving through an
electric potential of 1V. We get the following relation between Joule and one electron volt:
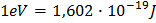
We often use energies which are of the order of several million electron volts so it is convenient to introduce the following
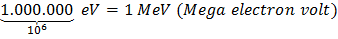
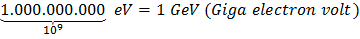
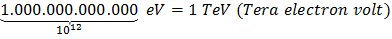
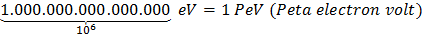
Conversion
To convert let's say 14 TeV (proton-proton collision energy at LHC when at full operation) to Joule you use the formula just above and you get:
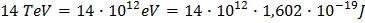
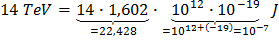
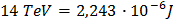
which is pretty much the energy of a flying mosquito!
Now what if you have a measurement in Joule and want to convert it into eV? You simply do:
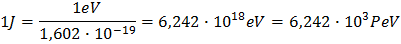
So you see, 1 Joule is about 6 thousand PeV. 1 Joule is how much kinetic energy a small apple attains after falling 1 meter in earths gravity.
Exercise (answers can be found at bottom of page)
- Convert 10 GeV into Joule.
- Convert 100 Joule into eV.
Here you get back to the measurement's main page.