Content
- Aims/Tasks
- Identifying particles
- Identifying events
- Measurement
- Concepts, definitions and methods
- Help 1: Energy units
- Help 2: Momentum
- Help 3: Vectors
- Help 4: Invariant mass
- HYPATIA and data samples
- Analysis
Invariant Mass
As you have already learned, the formula for relativistic energy of a particle is
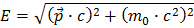
In order to calculate the mass of the Z boson we start with the formula for the Z mass as a sum of the energies and momenta of the decay particles:
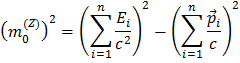
Since we are looking at Z decays into either an electron-positron pair or a muon-antimuon pair the sum is over two particles only, giving
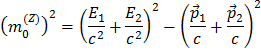
Multiplying out the parentheses:
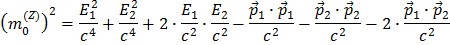
You recognize the
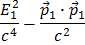 as
as 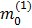 and likewise for particle 2, (from juggling around the terms in formula (1)).
and likewise for particle 2, (from juggling around the terms in formula (1)).
So you see that
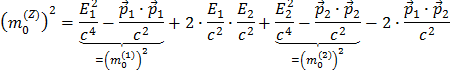
which, cleaned up, gives
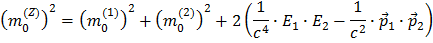
Taking the square root gives you the final expression of the Z mass expressed by the masses, energies and momenta of the two decay particles.
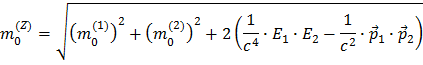
You therefore need to know all these quantities in order to calculate the Z mass.
Here you get back to the Z measurement site.